TAKE HEED!!
Test 4 on Monday November 10th
Exam on Monday November 17th
Study Guide
1. Functions of hormones:
Direct, control and regulate: Plant's patterns of growth and development.
Plant's responses to environmental conditions.
2. Main plant hormones:
Auxin, Cytokinin, Ethylene, Gibberellins, Abscisic Acid.
3. Compare the effect of auxins and cytokinins on plant growth:
Auxins stimulate cell elongation-----Cytokinins inhibit cell elongation (cells grow thicker)
Auxin inhibit lateral bud growth-----Cytokinins stimulate lateral bud growth.
Synthesized mostly in shoots--------Synthesizd mostly in roots.
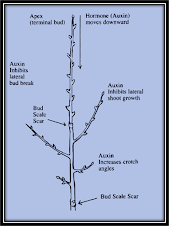
4. Main functions of Auxins:
-Cell elongation
-Induces shoot apical dominance (inhibit lateral bud growth).
-Inhibit abscission prior to formation of abscission layer.
-Involved in phototropism and gravitropism.
-Inhibit growth in high concentration (herbicides)
5. Stimulates fruit ripening-----------------------------------------Ethylene
Seed germination-----------------------------------------------------Ethylene- Gibberellins
Seed dormancy--------------------------------------------------------Abscisic Acid
Produced in response to stress---------------------------------Abscisic Acid- Ethylene
6. Hormone's rol in the leaf senescence:
Auxins: Inhibit abscission prior to formation of abscission layer.
Ethylene: Stimulates leaf senescence.
Gibberellins: Delays leaf senescence.
7. Hormone's rol in dormancy:
Cytokinins: Cause dormant seeds to sprout.
Gibberellins: Braking of dormancy.
Abscisic Acid: Encourages seed dormancy.
8. Plant responses to external stimuli:
- Tropisms (involve growth)
-Rapid responses (do not involve growth)
9. Plant tropisms:
-Gravitropisms: causes the root to grow with the force of gravity and the shoots against the force of gravity.
-Phototropism: causes the plant to grow toward the light.
-Thigmotropism: causes the plant to wrap tightly and atound any object they encounter.
10. Photoperiodisms:
Responsible for the timing of seasonal activities such as flowering and growth.
Causes the plant to respond to periods of light and darkness.
Shorth-day plants flowe when days are short.
Long-day plant flower when days are long.
Long-day plants bloom in the summer.
11. Phytochrome:
-Plant pigment.
-Responsible for photoperiodism.
-Regulates the changes in activity that prepare many plants for dormancy.
12. Dormancy:
-Is the period during which an organism's growth and activity decrease or stop.
- Deciduous plants turn off photosynthetic pathways----Transport material from leaves to roots.-----Seal leaves off from the rest of the plant.
13. Leaf Abscission:
a. Phytochrome absorb less light as days shorten.
b. Auxin production drops.
c. Ethylene production increses.
d. Chlorophyll (green pigment) synthesis stop. Carotenoids become visible.
e. Production of Anthocianins.
f. Nutient transport to other parts of the plant.
g. Abcission layer at the petiole seals the leaf off from the plant's vascular system.
h. Leaf falls to the ground.
14. Overwintering of Meristem
Hormones produce changes in apical meristem.
Produce thick, waxy scales that form a protective layer around new leaf buds.
15. Xerophytes' adaptations
nclude reduced permeability of the epidermal layer, stomata and cuticle to maintain optimal amounts of water in the tissues by reducing transpiration, adaptations of the root system (extensive roots) to acquire water from deep underground sources or directly from humid atmospheres. Storage of water in swollen stems (thinck stems) , leaves or root tissues. Reduced leaves. Seed that can be dormant many years.
16. Hydrophytes' adaptations
A thin cuticle. Cuticles primarily prevent water loss, thus most hydrophytes have no need for cuticles. Stomata that are open most of time: so water is abundant. A less rigid structure: water pressure supports them. Flat leaves on surface plants for flotation. Air sacs for flotation. Seeds that float. Smaller roots: water can diffuse directly into leaves. Feathery roots: no need to support the plant. Specialized roots able to take in oxygen. Airfilled spaces through which oxygen can diffuse.
17. Epiphytes' adaptations.
Use photosynthesis for energy and obtain moisture from the air or from dampness (rain and cloud moisture) on the surface of their hosts. Roots may develop primarily for attachment, and specialized structures (for example, cups and scales) may be used to collect or hold moisture.
18. Carnivorous plants
Obtain nutrients by trapping and digesting insects. Parasitic plants obtain nutrients from the tissues of other plants.
19 Chemical defense
19 Chemical defense
Some plants defend thenselves against insects attack by making compounds that are poisonous to animals or disrupt their growth and development.
20. Salt-tolerant adaptations
20. Salt-tolerant adaptations
Plants are able to pump excess salt out of tissues.
Review Content page 651.
21 What would happen if you accidentally planted a seed wrong side up?
The gravitopic response would cause the root to grow downward with the pull of gravity and the stem to grow upward against it.
22. Why are plant able to continue to grow as long as they live?
Because the top of each shoot has an apical meristem that contain cells that actively dividing (meristematic tissue).
23. Spinach is a long-day plant that grows best with a night length of 10 hour or less. Why is spinach not usually grown in region near the equator?
Nights near the equator are too long to allow spinach to grow properly.
Review Standardized Test Prep page 653.
GOOD LUCK GUYS!!




















12 comentarios:
wow Miss...that's a lot of content! but they move the test right? is not on Monday anymore?
okay miss....im getting prepared for it okay....jejejeje well ill try too...but you know that ill make it jajajajja bye take care
ahhh a proposito soy carlos boquin...el q dice anonimo sorry...jajajaj
miss the exam for 11th is monday???!!! no!!!!!!!!
and my exam of 10th is monday also???!!!! no!!!!!!!!!
and the work for 10th is monday also???!!!! no!!!!!!!!!
please no miss!!!!!! to much pressure I cant stand it!!! no!!!!
yo no sabia q abia examen!! :S
imaginense todo lo q puso solo para test...
el partial... bufff....
u r going to kill us miss!! apiadese de nosotros!!!! ;)
im so happy i got 96 on my test!!!! woooohoooo!!!!! :D im so happy!!!! :D!!!! i thank you because its so much better to study with your study guides!!! tnx!! att maria fernanda
Estimada Maestra, le agradesco la coloboración brindada a mi hija Angie y a todos los muchachos de onceavo grado.
Durante este periodo ha pasado pendiente de lo que sucediendo en el desarrollo de su catedra.
De ante mano gracias.
Pedro Ernesto
i gonna do my best in this test, trying to pass this class., jeje. thanks for all miss. stop writing onj the board.. jejeje. see you tommorow at the test, doing the herbarium. bye, luck friends.
JAJA!!!!! gracias miss...ve q le dije que es buena persona!!! yo sabia q iva a poner la guia para estudiar en el examen!!! jejeje de todos modos solo ocupo 4 puntos para pasar... :D jajaaj voy a ajustar el 4 de 20 en el examen...no mentira miss...chek gracias ahi nos vemos mañana
hey miss verdad que los que sacan mas de 80 tienen 5 puntos extras...
y como saque en biology 10mo mas de 80 tengo 5 puntos mas verdad...
por cierto yo escribi el mensaje pasado... Atte: David Kuan
No me recuerdo de mi password por eso me pongo como anonimo jejeje
Publicar un comentario