The graph shows how carrot cells respond to varying concentrations of auxins. Increasin auxin concentration is shown on the x-axis and plant growth is shown on the y-axis.
1. Maximum stem growth occurs at about 10-6 particle/L.
2. That concentration inhibits the growth of roots.
3. Concentration between approximately 10-9 and 10-3 particles/L promote stem growth. Concentration above about 10 -2 particles/L inhibit stem growth.
4. Because carrots are roots, a concentration of approximately 10-10 to 10-9 particles/L would produce the largest-sized carrots.
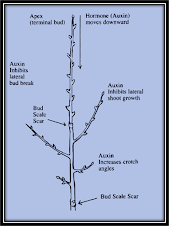
1. They control a plant’s branching pattern, the rate at which its stems elongate, and its responses to environmental conditions.
2. Auxins: stems and roots (cell elongation and differentiation), lateral buds (inhibit i. e. apical dominance). Cytokinins: lateral buds (stimulate growth), seeds (cause dormant seed to sprout), leaves (stomatal opening). Gibberellins: stem (cell elongation), seed (braking of dormancy, germination) root (inhibit growth). Ethylene: fruit ripening, flower and leaf senescence, seed germination.
3. Auxins stimulate cell elongation: cytokinins inhibit elongation and cause cells to grow thicker. Auxins inhibit lateral bud growth; cytokinins stimulate lateral bud growth. Auxins are synthesized in much greater amount in the shoots than in roots, Cytokinins and sinthesized in much greater amounts in thee roots than shoots.
4. The person will know to remove the apical meristem to make the tree grow rounder and fuller or leave it to make the tree grow taller and narrower.
5. The seedling curved because there was more auxin on the shaded side of the stem.




















1 comentario:
Exellent...I have all the answers...
Publicar un comentario